SAP FICO Certification Training
SAP FICO Online Training is a course that enhances the career opportunities of Finance professionals. SAP FI provides one of the most comprehensive worldwide financial management solutions available today. SAP CO supports coordination, monitoring, and optimization of all the processes in an organization. SAP FICO is very easy to understand and it is more flexible. Our online training program on SAP FICO will help you in understanding the core-concepts of Finance and Controlling modules. This is “certificate-ready” training program. By enrolling to our training program, you will get immense knowledge on Finance management that includes accounting, auditing and controlling which is constantly changing. Our training ensures that you can start your career in SAP FICO in an unsupervised environment as we do provide practical sessions that helps you to master in the subject. We provide case studies and updated study materials that will help you to get certified. Enroll now and Start learning SAP FICO from Industry Experts at UpTaught.
-
LevelAll Levels
Start Date
Time
Duration
Type
Mode of Training
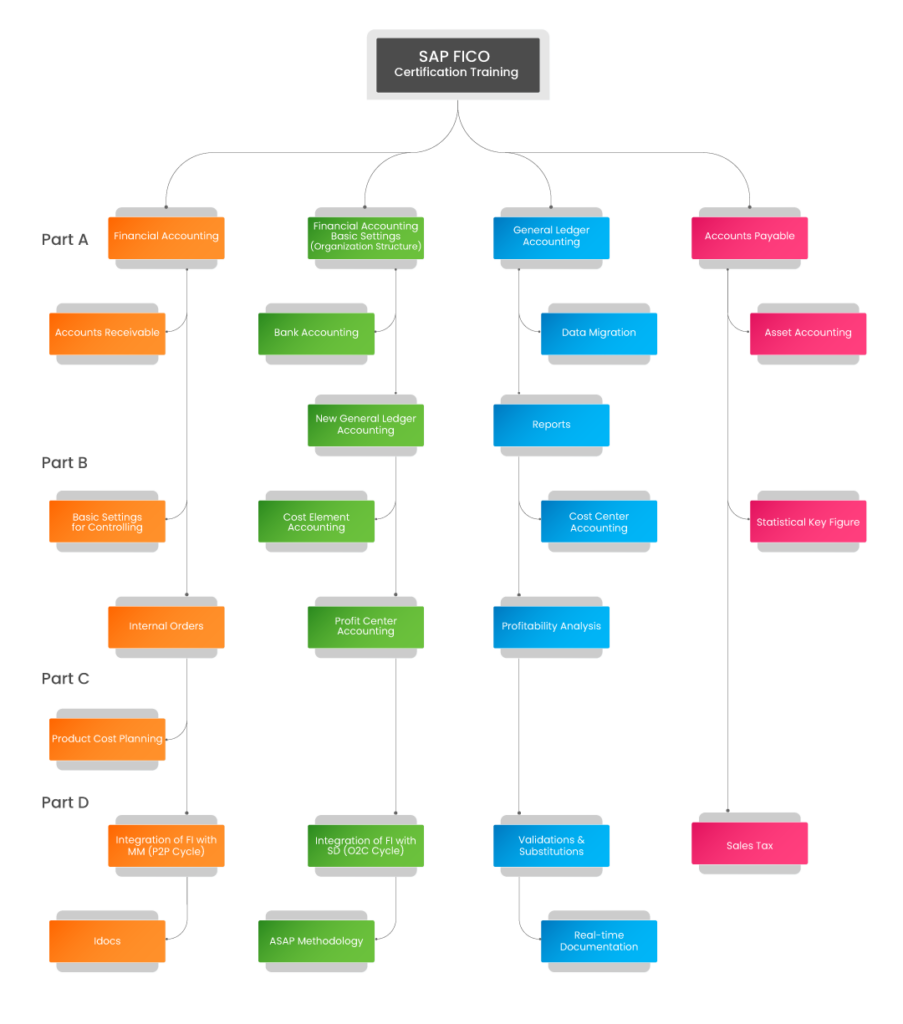
Course Curriculum
Part A – Financial Accounting
Module 2 – Financial Accounting Basic Settings (Organization Structure)
-
1. Definition of company
-
2. Definition of company code
-
3. Assignment of company to company code
-
4. Definition of business area
-
5. Definition of Chart of accounts and types of chart of accounts
-
6. Assignment of chart of accounts to company code
-
7. Definition of Account groups
-
8. Defining Retained Earnings Account
-
9. Definition of fiscal year variant, Short-end fiscal year
-
10. Assignment of fiscal year variant to company code
-
11. Definition of posting period variant
-
12. Assignment of posting period variant to company code
-
13. Open and close FI posting period
-
14. Defining document type & number ranges (internal and external)
-
15. Maintenance of field status variants
-
16. Assignment of field status variant to company code
-
17. Definition of tolerance groups for GL accounts
-
18. Definition of tolerance groups for employees
-
19. Assignment of tolerance groups to users
-
20. Global parameters
Module 3 – General Ledger Accounting
-
1. Creation of General Ledger Master (with and without reference)
-
2. Display/Change/Block/Unblock of general ledger master
-
3. Document Entry posting: normal postings and posting with reference
-
4. Display and change of documents
-
5. Display of GL balances
-
6. Display GL account line items
-
7. Parked documents
-
8. Hold documents
-
9. Creation of Sample Document and postings with sample documents
-
10. Creation of account assignment model and posting
-
11. Configuration of line layouts for display of GL line items
-
12. Accrual and Deferral documents
-
13. Reversal of individual documents, mass reversal, reversal of cleared items and reversal of accrual and deferral documents, re-reversal
-
14. Types of clearing – standard, partial and residual
-
15. Defining Exchange Rate types, Forex table and Translation and tables
-
16. Define Exchange rates & posting of foreign currency transactions
-
17. Interest calculations on term loans
-
18. Recurring documents
-
19. Tables and reports in GL
Module 4 – Accounts Payable
-
1. Creation of vendor account groups
-
2. Creation of number ranges for vendor master records
-
3. Assignment of number ranges to vendor account groups
-
4. Creation of tolerance group for venders
-
5. Creation of vendor master (display/change/block/unblock of vender master) and related tables
-
6. Posting of vendor transactions (invoice posting, manual payment posting, credit memo) and related tables
-
7. Settings for advance payments to parties (down payment) and clearing of down payment against invoices (special GL transactions)
-
8. Posting of partial Payment & Residual Payment
-
9. Cash discounts from vendors and payment terms
-
10. Automatic payment program configuration with SEPA format
-
11. Bank master data and house banksF110 execution – main bank posting from F110 and bank clearing account posting from F110 and related tables
-
12. DME files creation in xml and txt format and understanding DME structure in DMEE
-
13. Payment advice generation, payment summary generation
-
14. Reversal of payment documents
-
15. Vendor clearing – standard, partial and residual
-
16. Check payment method and create checks manually and automatically and print
-
17. Creation of check lots and maintenance of check register
-
18. Check encashment dates
-
19. Cancellation of unissued checks and issued checks
-
20. Creation of void reasons
-
21. Issued check cancellation
-
22. Deleting manual checks and voided checks
-
23. Defining correspondence & party statement of accounts
-
24. Real-time scenarios on APP
-
25. Intercompany payments – manual and automatic
-
26. Tables and reports in AP and APP
Module 5 – Accounts Receivable
-
1. Creation of customer account groups
-
2. Creation of number ranges for customer master records
-
3. Assignment of number ranges for customer account groups
-
4. Creation of tolerance group for customers
-
5. Creation of customer master (display/change/block/unblock of vender master) and related tables
-
6. Posting of customer transactions (sales invoice posting, manual payment posting, debit memo) and related tables
-
7. Settings for advance payment from parties (down payment)Configuration of settings for dunning and generating the dunning letters
-
8. Defining correspondence and party statement of accounts
-
9. Cash discounts to customers
-
10. APP configuration for incoming payments direct debit
-
11. Customer clearing – standard, partial and residual
-
12. Tables and reports in AR
Module 6 – Bank Accounting
-
1. House bank
-
2. Bank key
-
3. Bank account
-
4. Bank clearing accounts
-
5. Electronic bank statement (EBS): Configuration and execution MT940
-
6. Auto Lockbox: Configuration and execution
-
7. Cash journal/SAP query
Module 7 – Data Migration
-
1. LSMW (master data)
-
2. BDC (transaction data)
Module 8 – Asset Accounting
-
1. Defining chart of depreciation, depreciation areas
-
2. Creation of 0% tax codes for sales and purchases
-
3. Assignment of the chart of depreciation to company code
-
4. Defining account determination
-
5. Definition of screen layout rules
-
6. Definition of number ranges for asset classes
-
7. Integration with General Ledger & Posting rules
-
8. Defining Depreciation key
-
9. Definition of multilevel methods
-
10. Definition of period control methods
-
11. Creation of main asset master records
-
12. Creation of sub-asset master records
-
13. Acquisition/purchase of fixed assets
-
14. Sale/retirement of fixed assets
-
15. Transfer of assets (intra and intercompany)
-
16. Scrapping of assets
-
17. Depreciation run
-
18. Asset history report, Asset explorer and Asset documents
-
19. Line item Settlement of assets under construction of capital work in progress
-
20. Year-end activities
-
21. Asset mass changes
-
22. Tables and reports in AA
Module 9 – New General Ledger Accounting
-
1. Parallel ledgers
-
2. Document splitting
Module 10 – Reports
-
1. Financial statement version (FSV)
Part B – Controlling
Module 1 – Basic Settings for Controlling
-
1. Defining Controlling Area
-
2. Defining Number ranges for Controlling Area
-
3. Maintain versions
Module 2 – Cost Element Accounting
-
1. Creation of primary cost elements from FI and CO
-
2. Manual and automatic creation of primary and secondary cost elements
-
3. Grouping of cost elements
-
4. Change cost element master records
-
5. Primary cost element categories and Secondary cost element categories
-
6. Default account assignments
Module 3 – Cost Center Accounting
-
1. Defining Cost Center Standard Hierarchy
-
2. Creation of Cost Centers and cost center groups
-
3. Display and change cost center master records
-
4. Creation of cost center groups
-
5. Actual posting to cost centers
-
6. Reposting of CO line items
-
7. Repost of costs
-
8. Planning for cost centers
-
9. Actual and variance reports
Module 4 – Statistical Key Figure
-
1. Statistical Key figure
-
2. Creation and execution of Distribution Cycle with/without SKF
-
3. Creation and execution of Assessment cycles with/without SKF
-
4. Creation and execution of Actual periodic reposting
Module 5 – Internal Orders
-
1. Defining order types
-
2. Creation of internal order master records
-
3. Display and change internal order master records
-
4. Postings to internal orders
-
5. Planning for internal orders
-
6. Reposting co line items for internal orders
-
7. Repost of costs for internal orders
-
8. Report of Actuals and Variance analysis for internal orders
-
9. Creation of real and statistical internal orders
-
10. Posting of business transaction to real orders
-
11. Definition of allocation structures
-
12. Definition of settlement profiles
-
13. Definition of planning and budget profiles
-
14. Settlement of real internal orders
-
15. Budgeting and availability control
-
16. Maintain number ranges for budgeting
-
17. Define tolerances for availability control
-
18. Specification of exempt cost elements from availability control
-
19. Maintenance of budget manager
-
20. SAP Business workplace
Module 6 – Profit Center Accounting
-
1. Basic Settings for Profit Center Accounting
-
2. Creation of Dummy Profit Centers
-
3. Maintenance of control parameters for actual postings
-
4. Maintaining planning versions for profit centers
-
5. Maintenance the number ranges for profit center documents
-
6. Creation, change and display of profit center master records
-
7. Creation of revenue cost elements
-
8. Automatic Assignment of Revenue elements for Profit Centers
-
9. Assignment of profit centers in cost center master records
-
10. Creation of account groups in profit center accounting for planning
-
11. Planning for profit and loss account items
-
12. Planning for balance sheet items
-
13. Posting of transactions into profit centers
-
14. Generating the variance reports for profit and loss account items
-
15. Generating the variance reports for balance sheet items
-
16. Transferring balances from one PC to another PC
Module 7 – Profitability Analysis
-
1. Maintaining the operating concern and related tables
-
2. Define profitability segment characteristics
-
3. Assignment of controlling area to operating concern
-
4. Activating the profitability analysis
-
5. Define number ranges for actual postings
-
6. Mapping of SD conditions types to COPA value fields
-
7. PA transfer structure
-
8. COPA document generation from Billing and FI document
-
9. Creation of reports – Report painter
-
10. Viewing the reports
Part C – Product Costing
Module 1 – Product Cost Planning
-
1. Creation of bill of materials BoM
-
2. Creation of activity type master records
-
3. Planning for activity hours
-
4. Activity type price calculation
-
5. Creation of work center master records
-
6. Creation of routings
-
7. Defining cost sheet (overhead structures)
-
8. Assignment of cost sheet to costing variant
-
9. Cost component structure
-
10. Creation of cost estimate with quantity structure
-
11. Marking
-
12. Releasing – price change document
-
13. Creation of cost estimate without quantity structure
-
14. Additive costing
-
15. Base planning object (Reference or Simulation costing)
Part D – Integration
Module 1 – Integration of FI with MM (P2P Cycle)
-
1. Definition of organizational units in materials management i.e. plant, storage location and purchase organization
-
2. Assignment of organizational units to each other
-
3. Definition of tolerance groups for purchase orders
-
4. Definition of tolerance groups for goods receipt
-
5. Definition of tolerance groups for invoice verification
-
6. Definition of vendor specific tolerances
-
7. Creation, display and change of material master records
-
8. Creation of plant parameters
-
9. Maintenance of posting periods for materials management
-
10. Maintenance of parameters for invoice verification
-
11. Maintenance of plant parameters for inventory management and physical inventory
-
12. Definition of attributes for material types
-
13. Assignment of GL accounts for material transactions in financial accounting (Integration of MM with FI)
-
14. Valuation classes, Valuation grouping code
-
15. Creation of purchase order, posting of goods receipt, invoice verification and Goods issue for production
-
16. Price control – standard and moving average with postings
-
17. GR/IR clearing from F.13MM Pricing procedure and adding freight to pricing procedure
-
18. Stock report MB5B
Module 2 – Integration of FI with SD (O2C Cycle)
-
1. Definition of sales organization
-
2. Definition of distribution channels
-
3. Definition of divisions and Sales area
-
4. Assignment among various organizational units in SD
-
5. Definition of partner functions
-
6. Definitions of shipping point and loading points
-
7. Definition of pricing procedures
-
8. Determining the shipping points
-
9. Determining the pricing procedures
-
10. Maintenance of SD condition types
-
10. Maintenance of SD condition types
-
11. Maintenance of condition records
-
12. Assignment of GL accounts for sales transactions (integration of FI with SD)
-
13. Creation of sales order
-
14. Initialization of stock
-
15. Posting the delivery of goods with PGI
-
16. Creating the sales invoice
-
17. SD pricing procedure
Module 3 – Validations & Substitutions
-
1. Line item level
-
2. Header level
Module 4 – Sales Tax
-
1. Input tax
-
2. Output tax
-
3. Sales tax procedure
Module 5 – Idocs
-
1. Structure of an Idoc
-
2. AL11 path, Uploading and downloading files from AL11
-
3. Testing and copying an Idoc
-
4. Reprocessing an Idoc
Module 6 – ASAP Methodology
-
1. Phases in ASAP methodology
-
2. Project plan
Module 7 – Real-time Documentation
-
1. Business blueprint (BBP)
-
2. Estimate
-
3. High level design
-
4. Functional specifications
-
5. Test script
-
6. UAT
SAP FICO Certification Training
-
LevelAll Levels

Aruna
CERTIFIED SAP FI & CO WITH ECC AND S4 HANA
- Has overall 15 years of experience.
- 9 years of experience with respect to SAP FICO
- Has keen knowledge in controlling module
- Specialization in Core banking, Has exposure to S4HANA as well.
- Has vast knowledge in SAP FICO and helped more than 300 students to get certified.
- Excellent communication skills and has more than 7 years of experience in training the students across the globe.
Roadmap
Salary range
FAQs
As the market is emerging, massive industries are implementing, in the next five years, there will be a huge demand in the financial perspective. There are very limited certified SAP FICO Consultants with complete subject knowledge in the market. Thus we can expect more demand for FICO consultants in the near future.
Yes, SAP FI certification is worth it in recent times and will stay significant for the future as well.
- Associate-level SAP certification exam cost is 350 Pounds
- Professional-Level SAP certification exam cost is 430 Pounds
The average salary of an SAP ECC consultant is US$ $93,908.
Here are some of the job roles for which you are eligible:
- SAP Consultant
- IT Developers and Testers
- BI and reporting professionals
- Project Managers
- Data Scientists
The following are the different industries that are looking for SAP Consultants:
- Information Technology
- Telecommunications
- Operational Reports and Analytical Business Automobile
- Oil and Gas
- Consumer Products
- Engineering
- Construction
- Operations
- Healthcare
- Industrial Machinery and Components
- Utility
- Government Sector
Major companies that are hiring SAP ECC FI certified professionals are:
- PWC
- Bristlecone
- EY
- Deloitte
- SAP
- Infosys
- TCS
The following are the top SAP ECC Consultant skills that every consultant must have:
- General Ledger Accounting
- Accounts Payable
- Asset Accounting
- Reporting
- Accounts Receivable
- Financial Closing
- SAP Financial Basics
It is not tough if you follow a precise learning path and become easy to ace the SAP FICO certification. Before starting the preparation, focus on the Exam Objectives, check for good preparation resources.
No, FI is a difficult and critical module where the system needs to accomplish business, statutory, legal and mandatory necessities. You have to put lot of practice to understand the terminologies and Financial Accounting.
SAP FICO is one of the SAP core modules and is deeply integrated with other modules such as SAP Sales and Distribution (SAP SD), Sales Material Management (SAP MM), SAP Production Planning (SAP PP), and so on.
SAP FICO is the pillar of SAP as this is an outstanding application for finance-related functions and is one of the most demanding products.
SAP FICO and Oracle financials are demanding in the specific field. But most of the manufacturing companies choose SAP FICO.
You require a Minimum 1 year of SAP Implementation Experience or 2 years of Support experience with a minimum of 6 months experience in the module and version in which you desire to take up certification.
You can also cross-train yourself into advanced modules like CO, SAP S/4HANA Finance, BPC, BI, FSCM, etc.





